OWASP Smart Contract Top 10
By focusing specifically on smart contracts, the top 10 provides targeted insights into the unique challenges and threats of blockchain-based applications.

Table of content
The OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 is an important document aimed at helping developers and security professionals in the Web3 space understand and mitigate the most critical vulnerabilities commonly found in smart contracts. This initiative builds on the traditional OWASP Top 10 framework, which has been a cornerstone in web application security for many years. By focusing specifically on smart contracts, the document provides targeted insights into the unique challenges and threats of blockchain-based applications.
Here are some key aspects of the OWASP Smart Contract Top 10:
- Purpose: To raise awareness and provide guidance on the most prevalent and impactful vulnerabilities in smart contract ecosystems. This serves both educational and practical purposes, aiding developers in writing safer code and helping security teams in identifying and mitigating risks.
- Comprehensive Coverage: While the Top 10 list highlights the most critical vulnerabilities, it is also intended to be used in conjunction with other security projects and frameworks to ensure a more comprehensive understanding and management of risks associated with smart contracts.
- Resource for Developers: By providing examples, potential mitigations, and impacts of these vulnerabilities, the document serves as a valuable resource for developers who are building, deploying, and maintaining smart contracts.
- Evolving with the Ecosystem: The threats and security landscape in the blockchain space are rapidly evolving. The Smart Contract Top 10 aims to stay current by continuously incorporating recent data and insights from both security incidents and advancements in smart contract technology.
- Community Collaboration: OWASP projects often benefit from community contributions and collaboration, ensuring that the guidelines are reflective of the collective experience and expertise of developers and security professionals worldwide.
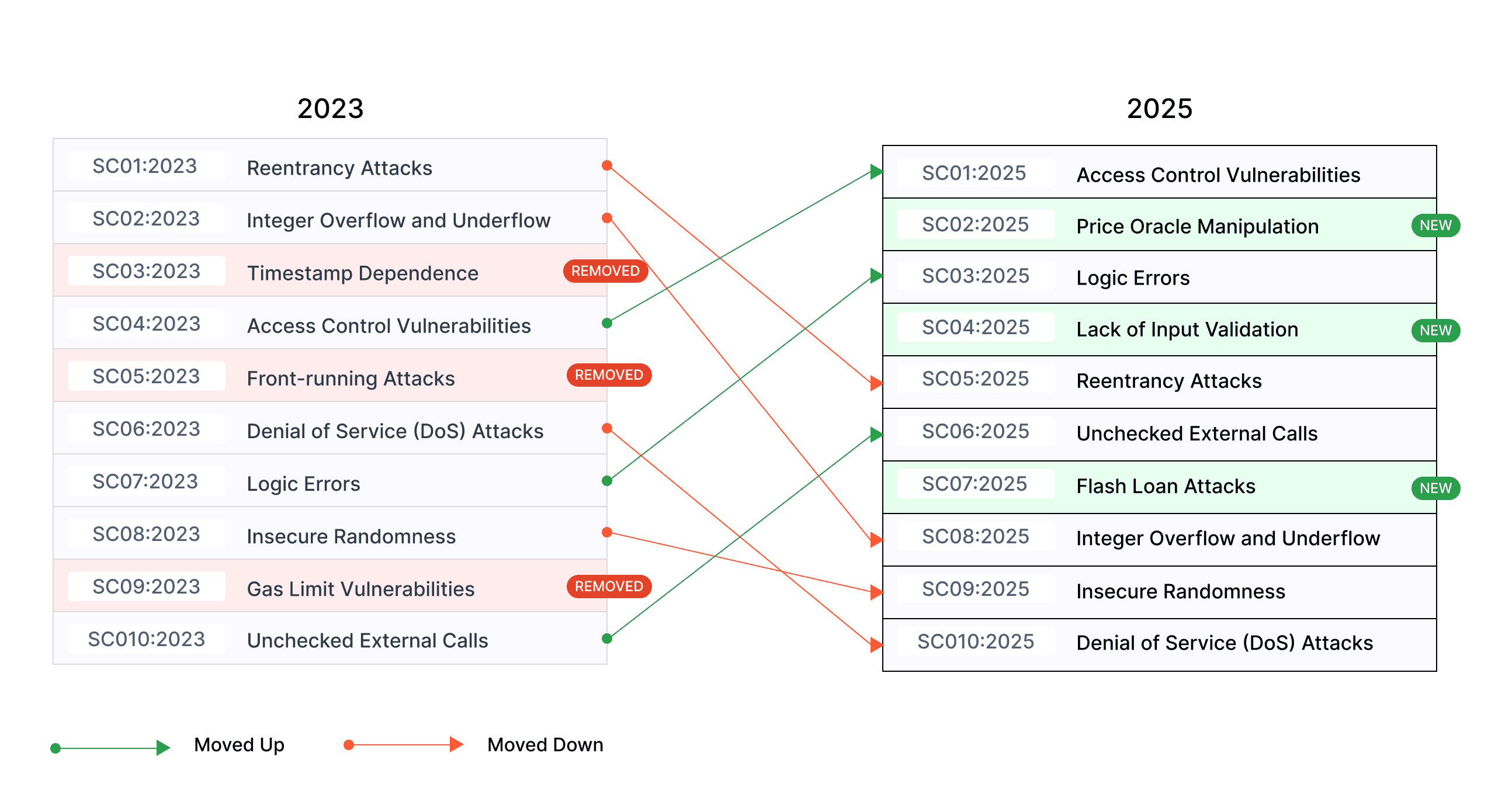
Changes in the Top 10 - 2025 vs 2023
Top 10 Vulnerabilities in 2025 According OWASP
SC01:2025 - Access Control Vulnerabilities
Access control vulnerabilities occur when unauthorized users are able to access or alter a contract's data or functions. These flaws arise when the code does not adequately enforce permission checks, potentially resulting in serious security breaches.
SC02:2025 - Price Oracle Manipulation
Price Oracle Manipulation takes advantage of weaknesses in the way smart contracts retrieve external data. Attackers can influence contract operations by altering or controlling oracle feeds, potentially causing financial losses or system instability.
SC03:2025 - Logic Errors
Logic errors, also known as business logic vulnerabilities, happen when a contract's actions differ from its intended design. This can manifest in issues such as improper reward distribution, problems with token minting, or errors in lending and borrowing logic.
SC04:2025 - Lack of Input Validation
Insufficient input validation can result in vulnerabilities where an attacker can exploit the contract by supplying harmful or unexpected inputs, potentially disrupting logic or triggering unexpected behaviors.
SC05:2025 - Reentrancy Attacks
Reentrancy attacks take advantage of the ability to call a vulnerable function again before it finishes executing. This can cause repeated state changes, potentially resulting in depleted contract funds or disrupted logic.
SC06:2025 - Unchecked External Calls
Not verifying the success of external function calls can lead to unintended consequences. If the called contract fails, the calling contract might continue erroneously, jeopardizing its integrity and functionality.
SC07:2025 - Flash Loan Attacks
Flash loans, although beneficial, can be abused to manipulate protocols by performing multiple actions within one transaction. Such attacks can lead to depleted liquidity, price manipulation, or exploitation of business logic.
SC08:2025 - Integer Overflow and Underflow
Arithmetic errors from exceeding the limits of fixed-size integers can create significant vulnerabilities, like incorrect calculations or token theft. Unsigned integers wrap around when they underflow, whereas signed integers can flip between extreme values.
SC09:2025 - Insecure Randomness
Generating secure randomness is challenging in blockchain networks due to their deterministic nature. If randomness is predictable or can be manipulated, it may lead to exploitation in areas like lotteries, token distributions, or other functionalities that rely on randomness.
SC10:2025 - Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks take advantage of vulnerabilities to deplete contract resources, making it non-functional. This can occur through excessive gas consumption in loops or function calls intended to disrupt the contract's normal operation.
Conculsion
To get the most current information or contribute to the OWASP Smart Contract Top 10, you can visit scs.owasp.org. This site offers more details on ongoing projects, additional resources, and ways to engage with the community working on improving smart contract security.
Contact
Curious? Convinced? Interested?
Schedule a no-obligation initial consultation with one of our sales representatives. Use the following link to select an appointment:
